Theme: Scoping out Latest exploration in Applied Microbiology & Future Trends of Beneficial Microbes
Applied Microbes 2021
About Conference:
Applied Microbes 2021 greets all Physicians, Pharmacists, Scientists, Young Researchers, Healthcare Industrial Delegates and Talented Student Communities in the field of Microbiology Department to attend this 6th World Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes, where all the phases of applied microbiology and beneficial microbes will be discussed under single roof. Applied Microbes 2021 will be an excellent amalgamation of academia and industry as it involves every aspects of empirical and conceptual thinking in exploring new dimensions in this field. It is open to all types of research methodologies both from academia and industry.
Microbiology is a division of science related discipline that contracts with the structure and function of microbes and the use and application of microorganisms for human benefit. Its applications comprise enormous subject including biotechnology, enzyme technology, medicinal microbiology, agricultural biotechnology, bioremediation, petroleum microbiology, microbial biofilms and food microbiology. Microbiology can be also classified based on taxonomy, as bacteriology, virology, mycology, protozoology, and phycology. Therefore, to acquire all this knowledge we heartedly invite you to join us at the Applied Microbes 2021, where you will gather amazing ideas and have a great experience with experts from around the world.
Why to Attend Applied Microbes 2021?
Applied Microbes 2021 highlights the theme “Discovering the New Inventions in Microbiology” With members from around the world focused on learning about applied microbiology and beneficial microbes and its advances in invention of Pharmaceutical, Food, Brewing Industries, Clinical Healthcare Systems , Hospitals and Research Organizations. This is the best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the Applied Microbiology community conduct presentations, distribute information, meet with current and potential scientists, and make a splash with new Medical techniques in recent trends.
APPLIED MICROBES 2021, will be the greatest podium for all the Microbiologist, Scientists, Research Scholars, Students, Technologists who are working in this field to exchange their knowledge related to microbial interactions its evolution, diversity, and role. This International occasion is an exertion to find information that will designate the possible interactions between the organisms and conducting such experiments, new techniques that will lead to the formulation of control measures, often using an alteration of the environmental factors for regulation of the microbial ecologies.
Opportunity to meet extremely famed speakers, researchers, specialists, Business giants, and the most up to date refreshes in Microbiology world are important for this conference leads to significance of this gathering.
- This is the greatest podium to grow new partnership & collaborations.
- For speeding up your route this is the best location into every territory in the entire World.
- In our Conference 89% attendees who are the Key contact in labs purchasing decisions.
- During this conference, Our Exhibitors were visited 4-5 times by 80% of the attendees.
- By this conference grid can be developed with both Academic and Business.
Importance and Scope:
Microbiology is one of the furthermost rapidly developing fields in today’s world. It is an important outlet in life science that promotes the healthy living of humans and other living organisms. The microbes affect almost every activity of our life including food, shelter, clothing, health etc. With-in the development in field of microbiology the effects of micro-organisms on human beings has been reduced to a greater extent. The arena of microbiology has its impact in many fields thus producing advanced techniques to diagnose and treat infectious diseases, and production of antibiotics, food products and management of waste products in an effective manner. Without microbiology these expansions in science ground would have been a fantasy.
Target Audience:
- Researchers & Fellowship
- Microbiologists
- Bacteriologists
- Virologists
- Medical Microbiologists
- Mycologists
- Pathologists
- Pharmacists
- Epidemiologists
- Students & Professionals
- Health Care Associations & Societies
- Health Care Professionals
- Biomedical companies
- Food & Beverage industry
- Dairy and food sector industries
- Genetic engineering and Biotechnology researchers
- Research Institute
- Industrial Business Entrepreneurs
Microbiology Associations Globally:
- International Union of Microbiological Societies
- American Society for Microbiology
- Federation of European Microbiological Societies
- Society for Applied Microbiology
- Greek Society of Microbiology
- Association for General and Applied Microbiology
- Microbiological Society of Iceland
- Romanian Society for Microbiology
- Swedish Society for Microbiology
- Turkish Microbiological Society
- Society for Applied Microbiology
Sessions/Tracks:
Track 01: Microbiology & Microbes World
Microorganisms or microbes are minute organisms that exist as unicellular, multicellular, or cell clusters. Microorganisms are extensive in nature and are beneficial to life, but certain can cause serious harm. They can be divided into six major types: bacteria, archaea, fungi, protozoa, algae, and viruses. Microorganism is the word used in plural & microbe as singular (pure dictionary differentiation). Microbes are micro-organisms. They are so minute that you can't see them without a microscope. Microbes are easy to work with and thus provide a simple vehicle for studying the complex processes of life; as such they have become a powerful tool for studies in genetics and metabolism at the molecular level. This intensive probing into the functions of microbes has resulted in numerous and often unexpected dividends.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 02: Medical microbiology
Medical microbiology, the enormous subset of microbiology that is applied to medicine, is a dissection of medical science concerned with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases. In accumulation, this arena of science studies various clinical applications of microbes for the improvement of health. There are four kinds of microorganisms that cause infectious disease: bacteria, fungi, parasites and viruses, and one type of infectious protein called prion. A medical microbiologist studies the characteristics of pathogens, their modes of transmission, mechanisms of infection and growth. The academic qualification as a clinical/Medical Microbiologist in a hospital or therapeutic research Centre generally requires a Masters in Microbiology along with Ph.D. in any of the life-sciences (Biochem, Micro, Biotech, Genetics, etc.).
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 03: Industrial microbiology
Industrial microbiology is a union of biotechnology that smears microbial sciences to create industrial products in mass quantities, often using microbial cell factories. There are numerous ways to operate a microorganism in order to increase maximum product yields. Introduction of mutations into an organism may be accomplished by introducing them to mutagens. Another way to increase production is by gene amplification, this is done by the use of plasmids, and vectors. The plasmids and/ or vectors are used to integrate multiple copies of a specific gene that would permit more enzymes to be produced that eventually cause more product yield. The impact of organisms in order to yield a specific product has many applications to the real world like the production of some antibiotics, vitamins, enzymes, amino acids, solvents, alcohol and daily products. Microorganisms play a big role in the industry, with multiple ways to be used. Medicinally, microbes can be used for creating antibiotics in order to treat antibiotics. Microbes can similarly be used for the food industry as well.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 04: Microbial biotechnology
Microbes (or microorganisms) are organisms that are too minor to be seen by the unaided eye. They include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, microalgae, and viruses. Microbes live in acquainted settings such as soil, water, food, and animal intestines, as well as in more extreme settings such as rocks, glaciers, hot springs, and deep-sea vents. The extensive variation of microbial habitats replicates an enormous diversity of biochemical and metabolic traits that have arisen by genetic variation and natural selection in microbial populations. Microbial biotechnology, enabled by genome revisions, will lead to breakthroughs such as enhanced vaccines and improved disease-diagnostic tools, improved microbial agents for biological control of plant and animal pests, alterations of plant and animal pathogens for reduced virulence, expansion of new industrial catalysts and fermentation organisms, and development of new microbial agents for bioremediation of soil and water contaminated by agricultural runoff.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 05: Food microbiology
Food microbiology is the study of the microorganisms that constrain, generate, or contaminate food. This contains the study of microorganisms triggering food spoilage; as well as, pathogens that might cause disease especially if food is improperly cooked or stored. Those used to produce fermented foods such as cheese, yogurt, bread, beer, and wine. Then those researchers with other useful roles such as producing probiotics. Food safety is a chief focus of food microbiology. Many agents of disease and pathogens are voluntarily transmitted via food which comprises bacteria and viruses. Microbial toxins are also possible contaminants of food; however, microorganisms and their products can also be used to combat these pathogenic microbes. Probiotic bacteria, including those that produce Bacteriocins can kill and inhibit pathogens. Instead, purified Bacteriocins such as nisin can be added directly to food products.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 06: Veterinary microbiology
Veterinary Microbiology deals with microbial (bacterial, fungal, viral) diseases of domesticated vertebrate animals (livestock, companion animals, fur-bearing animals, game, poultry, and fish) that supply food, other beneficial products or companionship. In accumulation, Microbial ailments of wild animals living in captivity, or as associates of the feral fauna will also be considered if the infections are of interest because of their interrelation with humans (zoonoses) and/or domestic animals. Studies of antimicrobial resistance are also included, provided that the results represent a substantial advance in knowledge. Veterinary microbiologists are veterinarians that specialize in the study of microorganisms that cause infectious disease in animal species. These disease-causing agents may contain bacteria, viruses, toxins, and parasites. They can also focus their research on one precise animal species or group of interest.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 07: Water microbiology
Bacteriological water investigation is a technique of analyzing water to estimate the numbers of bacteria present and, if needed, to find out what sort of bacteria they are. It represents one aspect of water quality. It is a microbiological analytical method which uses samples of water and from these samples controls the concentration of bacteria. It is then possible to draw implications about the appropriateness of the water for use from these concentrations. This process is used, for example, to routinely confirm that water is safe for human consumption or that bathing and recreational waters are safe to use. The elucidation and the action trigger levels for diverse waters vary depending on the use made of the water. Whilst very stringent levels apply to drinking water, more comfortable levels apply to marine bathing waters, where much inferior volumes of water are expected to be ingested by users.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 08: Applied Microbiology in Animals
Novel phases of applied microbiology in relation to animal health, it is projected to describe and enhance understanding of the role of microorganisms in animal health and disease, and provides a tremendous grounding in microbiology molecular biology, immunology and epidemiology. This grounding leads into the study of the complex mechanisms of host/microbe interactions that are involved in the pathogenesis of specific animal diseases, and provides insights into diagnosis and interventions, such as vaccines, essential for disease control.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 09: Forensic Microbiology
Forensic microbiology, like further zones of forensic science, deals with determining the cause of death and the identification of people who have committed crimes. A vital role of forensic microbiology is to regulate the “microbial signature” of an agent recovered in a criminal case. Forensic microbiology used in conjunction with forensic anthropology can be used to help trace individuals to specific areas. Forensic anthropologists, for example, often chart the migration patterns of ethnic groups through DNA analysis. These patterns -- and the microsatellites collected from specimens -- are recorded into databases.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 10: Pharmaceutical Microbiology
Pharmaceutical Microbiology is an applied branch of Microbiology. It involves the study of microorganisms associated with the manufacture of pharmaceuticals e.g. minimizing the number of microorganisms in a process environment, excluding microorganisms and microbial byproducts like exotoxin and endotoxin from water and other starting materials, and ensuring the finished pharmaceutical product is sterile. Other aspects of pharmaceutical microbiology include the research and development of anti-infective agents, the use of microorganisms to detect mutagenic and carcinogenic activity in prospective drugs, and the use of microorganisms in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products like insulin and human growth hormone.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 11: Oral Microbiology
Oral microbiology is the study of the microbes (micro biota) of the oral cavity and their connections between oral microorganisms or with the host. The environment extant in the human mouth is appropriate to the growth of characteristic microorganisms found there. It provides a source of water and nutrients, as well as a moderate temperature. Resident microbes of the mouth adhere to the teeth and gums to resist mechanical flushing from the mouth to stomach where acid-sensitive microbes are destroyed by hydrochloric acid. Oral bacteria have advanced mechanisms to sense their environment and avoid or modify the host. Bacteria occupy the ecological niche provided by both the tooth surface and gingival epithelium. However, a highly efficient innate host defense system constantly monitors the bacterial colonization and prevents bacterial invasion of local tissues.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 12: Molecular Bio robotics
It is a term representative of the amalgamation of several sciences. Under this banner, fields of bionics, genetic engineering and cybernetics are all in play. This collective study of different sciences coming together has allowed us to explore how robotics can interact with biology. In its wake, Bio robotics essentially allows robotics to be a substantial substitute for biological organism in a chemical as well as a mechanical capacity. Bio robotics replicates the biological understanding of living organisms and reproduces their characteristics through artificial means. The theoretical discipline of comprehensively engineering genetic information to develop new robotic designs is one aspect of Bio robotics. Another aspect is the use of biological specimens as components of a functioning robot.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 13: Host pathogen Interaction
The host–pathogen interface is distinct as how microbes or viruses sustain themselves within host organisms on a molecular, cellular, organismal or population level. This tenure is most usually used to refer to disease-causing microorganisms although they may not cause illness in all hosts. Because of this, the definition has been expanded to how known pathogens survive within their host, whether they cause disease or not. On the molecular and cellular level, microbes can infect the host and divide rapidly, causing disease by being there and causing a homeostatic imbalance in the body, or by secreting toxins which cause symptoms to appear. Viruses can also contaminate the host with contagious DNA, which can affect normal cell processes (transcription, translation, etc.), protein folding, or evading the immune response.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 14: Pale microbiology, Archaeomicrobiology & Microbial Forensics
Paleomicrobiology – Past Human Infections' features the approaches and main attainments in this emerging field of research at the intersection of microbiology and evolution, history and anthropology. New molecular approaches have already provided exciting results, such as confirmation of a single biotype of Yersinia pestis as the causative agent of historical plague pandemics, and the closer proximity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from ancient skeletons to modern strains than to Mycobacterium bovis, shedding new light on the evolution of major human pathogens and pathogen–population relationships. Firm microbiological diagnoses also provide historians and anthropologists with new data on which to base evaluation of past epidemics.
Microbial forensics states to the exploration of the use of bioweapon, and the accidental release or natural development of dangerous microorganisms. The span may also comprise the study of a person’s specific Microbiome for means of identification, the location of a crime and the time of death of an individual based on the progress of the Microbiome during decomposition.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 15: Geomicrobiology
Geomicrobiology is the scientific field at the intersection of geology and microbiology. It apprehensions the part of microbes on geological and geochemical processes and effects of minerals and metals to microbial growth, activity and survival. Such interactions occur in the geosphere (rocks, minerals, soils, and sediments), the atmosphere and the hydrosphere. Geomicrobiology studies microorganisms that are driving the Earth's biogeochemical cycles, mediating mineral precipitation and dissolution, and sorbing and concentrating metals. The requests include for example bioremediation, mining, climate change mitigation and public drinking water supplies.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 16: Prebiotics and Probiotics
Prebiotics are a sort of fiber that the human body cannot digest. They aid as food for probiotics, which are tiny living microorganisms, including bacteria and yeast. Both prebiotics and probiotics may support helpful bacteria and other organisms in the gut. Prebiotics and probiotics both support the body in building and maintaining a healthy colony of bacteria and other microorganisms, which supports the gut and aids digestion. These food mechanisms help endorse beneficial bacteria by providing food and creating an environment where microorganisms can flourish. Prebiotics are present in fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Probiotics occur in many fermented foods, including yogurt, sauerkraut, and tempeh.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 17: Soil Microbiology
Soil microbiology is the study of microorganisms in soil, their functions, and how they affect soil properties. It is believed that between two and four billion years ago, the first ancient bacteria and microorganisms came about on Earth's oceans. These bacteria could fix nitrogen, in time multiplied, and as a result released oxygen into the atmosphere. This led to more advanced microorganisms, which are important because they affect soil structure and fertility. Soil microorganisms can be categorized as bacteria, actinomycetes, fungi, algae and protozoa. Each of these clusters has features that define them and their functions in soil. Up to 10 billion bacterial cells inhabit each gram of soil in and around plant roots, a region known as the rhizosphere.
Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 18: Human Micro biota
The human Microbiome is the cumulative of all microbiota that reside on or within human tissues and bio fluids along with the consistent anatomical sites in which they reside, including the skin, mammary glands, placenta, seminal fluid, uterus, ovarian follicles, lung, saliva, oral mucosa, conjunctiva, biliary tract, and gastrointestinal tract. Kinds of human microbiota contain bacteria, archaea, fungi, protists and viruses. Though micro-animals can also live on the human body, they are typically excluded from this definition. In the atmosphere of genomics, the occupancy human Microbiome is occasionally used to rise to the collective genomes of resident microorganisms.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
Track 19: Host pathogen Interaction
The host–pathogen collaboration is defined as how microbes or viruses endure themselves within host organisms on a molecular, cellular, organismal or population level. This period is most frequently used to refer to disease-causing microorganisms although they may not cause illness in all hosts. Because of this, the definition has been prolonged to how known pathogens persist within their host, whether they cause disease or not. On the molecular and cellular level, microbes can infect the host and divide rapidly, causing disease by being there and causing a homeostatic imbalance in the body, or by secreting toxins which cause symptoms to appear. Viruses can also contaminate the host with virulent DNA, which can affect normal cell processes (transcription, translation, etc.), protein folding, or evading the immune response.
Related: Microbiology Conferences | Microbiology Meetings | Microbiology Congress | Applied Microbes | Microbiology Events | Applied Microbes Conferences
A microbe is a minute living organism, such as a bacteria, yeast, or fungus. Microbial products are formed by microbes and industrial microbiology is a division of biotechnology which contracts with the field. Microbes have been utilized for centuries to produce bread, cheese, wine, vinegar. Medicinal microbiology includes production of enzymes, antibiotics, nutrients such as amino acids, vitamins, and organic acids, chemotherapeutic agents, vaccines etc. Penicillin invention is a classic illustration of microbial product for medicinal use. Beer was the chief commercial product which dates back to about 1750 BC established by the ancient Sumerians. Another solicitation of microbial products is the creation of solvents and reagents such as ethanol, lactic acid, butanol etc. Synthesis of amino acids such as are L-Methionine, L-Lysine, L-Tryptophan, L-Glutamic acid etc. are additional use of industrial microbiology for manufacture of microbial products.
Fermentation technology is the furthermost applied way for manufacturing of microbial products which converts sugars into gas, alcohols or acids. Advances in fermentation technology have the potential to change the way microbial products are produced. Until recently, fermentation depended on limited raw materials and microbial strains which had a low yield. However, genetic recombinant technology is being used to control microbes to increase their productivity and make them capable to use a wide variety of raw materials. Reengineered microbes can yield microbial products more economically and naturally. Biotechnology has advanced to the level of engineering microorganisms to increase the yield of microbial products using ways such as introduction of mutations into an organism, gene amplification using plasmids, and vectors.
The market for microbial products is resolute by characteristics such as growing prevalence of diseases, increasing demand for healthcare nutrients such as vitamins, rising rates of cancers, rising demand for diagnostics microbial products, evolution of existences industry recommending many of these products etc. The constraints on the market are the highly fragmented nature of the industry, pressures on profits due to cut throat competition, secrecy surrounding the fermentation process, substandard and low quality producers operating from unknown locations etc.
Considering all these aspects, the market for microbial products identification and treatment is expected to reach $ 250.3 billion by the end of 2023; this market is projected to growing at a CAGR of ~ 8.7 % during 2017-2023.
Segments:
The worldwide microbial products market is segmented on the origin of categories, source, applications and end users. Based on categories, the market has been segmented as enzymes, polysaccharides, nutrients (amino acids, nucleotides, vitamins, and organic acids, others), chemotherapeutic agents, antibiotics, vaccines, others. Based on the source, the market has been segmented as bacterial, viral, fungi and others. Based on the applications, the market has been segmented as pharmaceutical, diagnostic, biotechnology and others. Based on the end users, the market has been segmented into pharmaceutical and biotechnological activities, hospitals & clinics, diagnostic labs, research & academics and others.
Regional analysis:
US accounts for the extreme market share due to favorable insurance penetration, excellent reimbursement scenario and greater expenditure on healthcare. The high per capita depletion of microbial products due to high per capita income also drives the market. The faster market uptake of new technology in the US is also an important driver of the market for global microbial products. Europe is the second largest market due to large disposable income and rising consumption patterns. Asia Pacific region is predictable to have the most forthcoming potential and it is estimated to be led by China and India. The Middle East & Africa market is led by the gulf nation’s predominantly Saudi Arabia and UAE. The regions of Africa are expected to witness a moderate growth due to poor economic and political conditions and poor healthcare penetration.
Key players of Global Microbial products market:
Key players profiled in the report are Amgen Inc., Merck & Co. Inc., Valent Biosciences Corp., and GlaxoSmithKline plc, Pfizer Inc., bioMérieux SA, Ajinomoto Co.Inc., Sanofi S.A, Novartis AG, NovaDigm Therapeutics, Kyowa Hakko Bio Co., Ltd. and others.
The report for Global Microbial products market by Market Research Future comprises of extensive primary research along with the detailed analysis of qualitative as well as quantitative aspects by various industry experts, key opinion leaders to gain a deeper insight of the market and industry performance. The report offers a clear picture of the current market scenario which contains past and estimated future market size with respect to value and volume, technological advancement, macro economical and governing factors in the market. The report affords detail evidence about and strategies used by top key players in the industry. The report also gives a broad study of the different market segments and regions.
Applied Microbiology size was valued at over USD 24.3 billion in 2017 and will exceed USD 675.2 billion with 7.9% CAGR from 2017 to 2024. At Global Market Insights, It is a single blend of primary and secondary research, with validation and iterations, in order to minimize deviation and present the most accurate analysis of the industry.
Graphical representation of Microbiology Market Analysis.
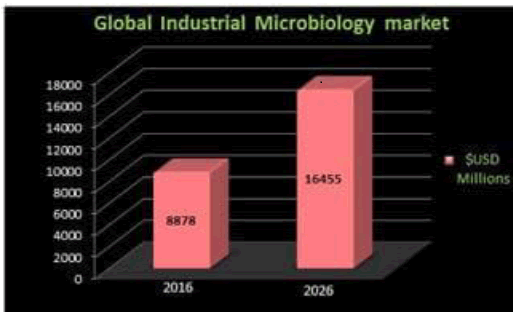
Expanding response of new technologies will drive the biotechnology industry size. we’ve seen tremendous evolution and variation in the industrial diagnostics industry, particularly in the food safety sector expertise in all aspects of the market, plus extensive experience in business management, strategy development and international business, microbiology test volumes, market values and methods used by food producers around the world, based on detailed interviews with more than 450 food production facilities in America, Europe and Asia, including Japan. Total test volumes have increased 128%, and testing for specific foodborne pathogens like Salmonella and E. coli grew at an even faster rate.
Applied Microbes 2020
We gratefully express thank all our pleasing speakers, conference attendees, students for making Applied Microbes 2020 Conference the best ever!
The “5th World Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes” was held during November 25-26, 2020 in Singapore City, Singapore based on the theme discovering the New Challenges in the field of Microbiology. The generous response was received from the Editorial Board Members of Journals along with scientists, researchers, students, and leaders from various fields of Microbiology, who made this event a grand success. We are acknowledging with gratitude and support by all the Editorial Board Members of Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials for their valuable suggestions for the growth of the Organization.
The conference was initiated with the Honorable presence of the Keynote forum. The heartfelt gratitude to the Organizing Committee Associates, many external experts, company representatives and other eminent personalities who supported the conference by facilitating the discussion forums. We also took the privilege to felicitate the Organizing Committee Members, Editorial Board Members and Media Partners who supported this event.
By the outstanding accomplishment of Applied Microbes 2020, it is proud to announce the “6th World Conference on Applied Microbiology and Beneficial Microbes” to be held during June 21-22, 2021 as a Webinar. Applied Microbes 2021 has been organized with the intention and the specific intent of promoting the development of new perspectives and ideas for exploiting the high level of Awareness attained by the scientific community in various Microbiology field.
Let us meet at @ Applied Microbes 2021
Conference Highlights
- Microbiology & Microbes World
- Medical microbiology
- Industrial microbiology
- Microbial biotechnology
- Food microbiology
- Veterinary microbiology
- Water microbiology
- Applied Microbiology in Animals
- Forensic Microbiology
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology
- Oral Microbiology
- Molecular Bio robotics
- Host pathogen Interaction
- Pale microbiology, Archaeomicrobiology & Microbial Forensics
- Geomicrobiology
- Prebiotics and Probiotics
- Soil Microbiology
- Human Micro biota
- Host pathogen Interaction
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 21-22, 2021 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Applied Microbiology: Open Access
- Clinical Microbiology: Open Access
- Journal of Microbial & Biochemical Technology
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



